AP3-HNN9-00 ionomer can be used as a coating and adhesive. The ink formula can be prepared for use in fuel cell catalyst layers. Usually, the ionomer is mixed with a suitable alcohol, then stirred and poured with an appropriate amount of catalyst powder and water droplets.
Aemion+ ™ It is an updated product line from Ionomr, with better chemical stability and durability, suitable for electrolysis. It is a breakthrough material that can continuously maintain complete stability in both strong alkaline and acidic environments, thereby achieving a wide range of innovative energy storage chemical compositions and configurations. This material has a hydrocarbon skeleton, which makes its impact on the environment smaller than ordinary fluorinated materials. By using advanced stabilization technology, Aemion ™ Being able to compete with the strongest substitutes.
Typical applications include metal air, nickel metal hydride, and solid-state battery chemistry. This highly conductive adhesive material has an affinity for negatively charged electrode components. It can be processed in low boiling solvents, used as an alkaline/acidic stable electrode coating or adhesive, and is highly customizable to optimize electrochemical performance, application scale, and manufacturing methods.
main features
Enabling systems without precious metals
High conductivity
Catalyst layer ionomer
The role of ion exchange polymers in hydroelectric electrolysis tanks and fuel cell membrane electrode assemblies
Membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs) are considered the core of hydroelectric electrolysis tanks and fuel cells. It consists of a gas diffusion layer (or porous transport layer), a catalyst layer (CLs), and an ion exchange membrane. MEA contains sites where significant electrochemical reactions occur. They are also responsible for the quality transfer process, including transferring reactants to the equipment and products to the equipment, as well as conducting electrons from the electrodes to the external circuits of the electrolysis tank and fuel cells. The performance of hydroelectric electrolysis tanks and fuel cells is greatly influenced by the GDL, CL, and membrane characteristics that make up MEAs. Electrodes should have high conductivity and porosity, while CL should have high catalytic activity. Ideally, MEA possesses all of these characteristics while being affordable. Especially for polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolysis cells and fuel cells, cost has always been a problem, as high acidic operating conditions require the use of expensive platinum group metal catalysts, usually Pt/C.
Balancing cost-effectiveness and device performance requires optimizing membrane electrode manufacturing. MEA is typically produced through two main technologies. Firstly, the gas diffusion electrode (GDE) method involves depositing a catalyst layer on GDL. Secondly, in catalyst coated membrane (CCM) technology, the catalyst is directly coated on the ion exchange membrane through electrostatic spraying, ultrasonic coating, sticker transfer printing, and screen printing. The CCM method produces membrane electrodes with lower interface resistance due to the reduction of reactant diffusion paths and the expansion of contact area. It should be noted that due to the high aggregation trend of catalyst particles and the evaporation of solvents used in ink formulations, direct deposition of the catalyst on the membrane may lead to the formation of cracks in the CL.
In order to improve the utilization rate of the catalyst, ion exchange polymers or ionomers are added to the catalyst ink formula. Catalyst ink formulations typically consist of catalysts, solvents, and ion exchange polymers or ionomers. The electrochemical performance, coating characteristics, and coating stability of CL highly depend on the interaction of these three main components. Ion exchange polymers adsorb onto catalyst particles in CL. This adsorption increases the surface charge of catalyst particle aggregates. Due to the dominance of electrostatic repulsion between catalyst particles in van der Waals forces, the trend of agglomeration formation decreases. Most importantly, ion exchange polymer particles increase steric hindrance, causing CL particles to move away from each other. In addition to improving the utilization of catalysts, ion exchange polymers can also improve charge (anion or proton) conduction as they serve as extended charge conductors for the main body of ion exchange membranes. Ions are also used as binders for catalyst particles, ensuring the existence of available reactant transfer and conductive pathways. Finally, ion exchange polymers act as hydrophilic agents to maintain optimal moisture content to ensure sufficient membrane moisture.
Solvent compatibility of anion exchange polymers
The way in which ionomers interact with solvents and catalysts is a key factor in determining the dispersion stability and rheological properties of ink. The following is applicable to Aemon+ ™ The solvent for AP3-HNN9-00.
| Solvent type | comment | Solubility wt% |
| Ethanol/acetone | 50:50 (v/v) mixture. Recommended low boiling solvent | 1% – 7% |
| Methanol/MEK | 50:50 (v/v) mixture | 1% - 6% |
| NMP, DMF | High boiling point solvents can cause Respiratory complications | 1% - 10% |
We sell ionomers in the form of pure polymer powders and provide customers with comprehensive processing and dissolution instructions to create our own solutions. This saves us and you the trouble of transporting flammable liquids, as well as related safety and cost considerations.
Both PEM and AEM are easily soluble in low boiling, common laboratory solvents.
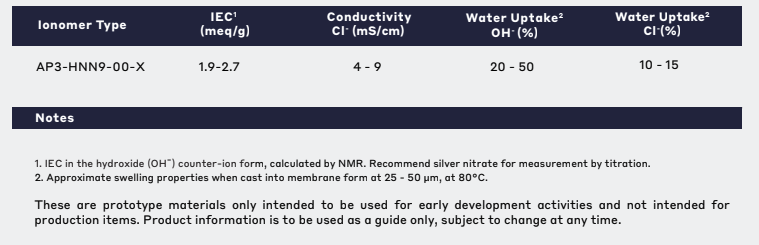
These are prototype materials used only for early development activities and not for production projects. The product information is for reference only and is not intended as a design specification, and may change at any time as part of ongoing product development. Ionomr makes no express or implied warranties, and assumes no obligation or responsibility for any results obtained by using or relying on this information.
 微信扫码 关注我们
微信扫码 关注我们

24小时咨询热线

移动电话13820242737
Copyright © 2024 All Rights Reserved. 地址:Building B1, No. 42 Haitai Avenue, Huayuan Industrial Zone, Binhai High tech Zone, Tianjin City -404 津ICP备2022004700号-1 XML地图